Developing on our local workstations has always been a conceptual challenge for my team when it comes to remote data access. Local workstation-based development of services that intend to connect to a wide range of remote services that may have no options for external connections poses a challenge. Mirroring the entire development environment is possible in many cases, just not practical.
In days before Kubernetes, writing code in IDEs on our local workstation meant we had only a few options for developing server-side-API-style services that needed to connect to a database. We could set up a database server on our local workstation manually or use packages like MAMP/WAMP, or run big virtual servers managed with Vagrant. Even after we got the database running, we needed a good set of data to work with, and that often meant asking a DBA or Sysadmin for SQL dumps from an environment in which we have no access.
Kubernetes gives us new ways to connect to remote services, some of these services are never intended to be connected to outside the cluster, having no ingress or firewall rules, yet we still need to connect from the outside when developing on a local workstation.
Port-forward a Kubernetes service:
kubectl port-forward svc/elasticsearch 9200:9200 -n the-project
In the command above, I’m forwarding the Kubernetes Service elasticsearch, and it’s port 9200 from the-project namespace to port 9200 on my local workstation. Studying this command may be enough to get you going, and if you followed my guide, Production Grade Elasticsearch on Kubernetes, you could run this same command.
If you don’t understand that command, or running it produces an error, read on.
Port Forward elasticsearch Kubernetes Service
Since Kubernetes v1.10, the command kubectl port-forward “allows using resource name, such as a service name, to select a matching pod to port forward to.” kubectl port-forward also works with deployments, daemon sets, replica sets and so on.
Get a list of services running in the-project namespace:
kubectl get services -n the-project
Services expose a port and map it to another port on a pod. In the case of connecting to Elasticsearch, we don’t care what pod we are connecting to, in fact, we want to connect the same way or application will, and that is through a Service. It so happens that the elasticsearch Service in the-project namespace uses Port 9200, the default for elasticsearch; however this could have easily been customized to some other port, and this is why we always want to list our services and ports they expose.
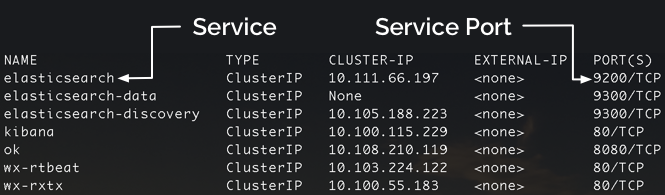
Now that we have the Service name and port we can issue a port-forward command with kubectl:
To port-forward the Elasticsearch Service to my local workstation I need to provide a local port that is available. I would need to choose a port other than 9200 if I had something already on that port.
kubectl port-forward svc/elasticsearch 9200:9200 -n the-project
The following diagram is a breakdown of the kubectl port-forward command:
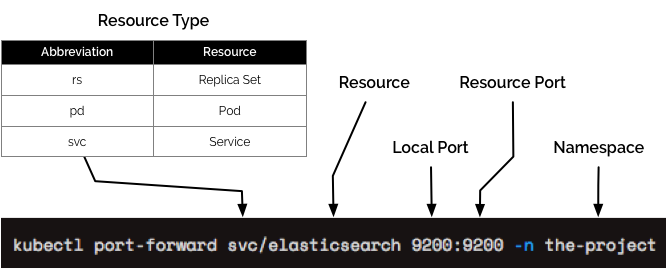
If the above command is running without error, open another terminal and use Curl to get the cluster stats:
curl "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/stats?human&pretty"
If the command above returned a large JSON object describing the Elasticsearch cluster in your Kubernetes environment, congratulations. If you encountered an error, read on.
Permission Denied
If kubectl port-forward claims you don’t have permission to port forward a Service on the cluster, you need to review the RBAC Permissions for the credentials used for remote access to the Kubernetes cluster.
If you are getting an error along the lines of 127.0.0.1:9200, 16): Connection refused it is most likely that Elasticsearch is not binding to all local interfaces on the Pod and is defaulting to its hostname. Since you can not provide a hostname through simple port-forward, you want to check your elasticsearch.yml configuration and ensure that Elasticsearch listens on all interfaces by specifying network.host: 0.0.0.0. However, if you are using the configuration from the article Production Grade Elasticsearch on Kubernetes, the value of network.host is set from the environment variable NETWORK_HOST for the Pod. See the Deployment for Client and Ingest Nodes configuration, paying special attention to the env: section where the environment variable setting NETWORK_HOST is 0.0.0.0.
Port-forwarding RBAC Permissions
In the article, Kubernetes Team Access - RBAC for developers and QA, I set up the Roles developer and deployer. In this example, I am using the kubectl config context with the developer service account. Whatever Role you are bound to must have the following RBAC rules applied to port forward:
- apiGroups:
- '*'
resources:
- 'pods/portforward'
- 'services/portforward'
verbs:
- create
See Roles and RoleBindings for a better understanding of how these rules apply to our access.
Postman
In the following examples, I use my favorite (and free) HTTP client, Postman. When working with HTTP based APIs, I typically use Postman. However, I’ll be exporting the Postman calls to curl commands so they can also be displayed here and tested on the command line.
If you want access to my Postman calls to run for yourself:
Query Elasticsearch Indices and Mappings
If the command kubectl port-forward svc/elasticsearch 9200:9200 -n the-project is running without error in a terminal we are ready to start working with Elasticsearch on our local workstation through port 9200.
Get Indices
Get a list of Indices:
curl -X GET \
'http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?format=json&pretty=true'
Output:
[
{
"health": "green",
"status": "open",
"index": ".kibana",
"uuid": "9qr9qjD4T1-2KhWi70zcYw",
"pri": "1",
"rep": "0",
"docs.count": "6",
"docs.deleted": "0",
"store.size": "33.1kb",
"pri.store.size": "33.1kb"
},
{
"health": "green",
"status": "open",
"index": "wx-rtbeat-2018.07",
"uuid": "nMHK2dxfTbmbnLubKvLTRQ",
"pri": "5",
"rep": "1",
"docs.count": "5566",
"docs.deleted": "0",
"store.size": "4.8mb",
"pri.store.size": "4.8mb"
}
]
The output of _cat/indices returns a JSON array of Indices. In the article, High Traffic JSON Data into Elasticsearch on Kubernetes I demonstrate collecting weather data from the Dark Sky API. The weather data populates an Elasticssearch index based on the year and month. As of the time of this writing, I only have one index wx-rtbeat-2018.07. The index .kibana is used by my Kibana service.
Get Index Mapping
The Get Mapping call gives us the field mapping of an index or a group of indexes. In this case, we want all of the fields any index starting with wx-rtbeat-* (* being a wildcard.) Postman generates the Curl call with the URL encoding %2A for the * character.
curl -X GET \
http://localhost:9200/wx-rtbeat-%2A/_mapping
Output:
{
"wx-rtbeat-2018.07": {
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"_meta": {
"version": "7.0.0-alpha1"
},
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"fields": {
"path_match": "fields.*",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
{
"strings_as_keyword": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
],
"date_detection": false,
"properties": {
"@timestamp": {
"type": "date"
},
"beat": {
"properties": {
"hostname": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"version": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
},
"clientIp": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"error": {
"properties": {
"code": {
"type": "long"
},
"message": {
"type": "text",
"norms": false
},
"type": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
},
"fields": {
"type": "object"
},
"rxtxMsg": {
"properties": {
"key": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"label": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"payload": {
"properties": {
"alerts": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"expires": {
"type": "float"
},
"regions": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"severity": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"time": {
"type": "float"
},
"title": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"uri": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
},
"currently": {
"properties": {
"apparentTemperature": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"cloudCover": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"dewPoint": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"humidity": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"icon": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"nearestStormBearing": {
"type": "long"
},
"nearestStormDistance": {
"type": "long"
},
"ozone": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"precipIntensity": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"precipIntensityError": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"precipProbability": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"precipType": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"pressure": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"summary": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"temperature": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"time": {
"type": "long"
},
"uvIndex": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"visibility": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"windBearing": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"windGust": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"windSpeed": {
"type": "half_float"
}
}
},
"latitude": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"longitude": {
"type": "half_float"
},
"offset": {
"type": "byte"
},
"timezone": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
},
"producer": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"seq": {
"type": "long"
},
"time": {
"type": "date"
},
"uuid": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
},
"tags": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
},
"type": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 1024
}
}
}
}
}
}
If you followed along with the High Traffic JSON Data into Elasticsearch on Kubernetes guide, the mapping returned by the _mapping call should match the fields.yml section of the wx-rtbeat ConfigMap.
Query Elasticsearch Data
Get the last ten minutes of weather data from our wx-rtbeat-* indices:
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:9200/wx-rtbeat-%2A/_search \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{ "query": {
"range" : {
"@timestamp" : {
"gt" : "now-5m"
}
}
}
}'
Output:
{
"took": 19,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "wx-rtbeat-2018.07",
"_type": "doc",
"_id": "pv8y2GQB4YMKAkYm7rjf",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"@timestamp": "2018-07-26T20:06:12.982Z",
"type": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"rxtxMsg": {
"producer": "cron",
"label": "/wx-data",
"key": "collector",
"payload": {
"longitude": -117.826581,
"offset": -7,
"timezone": "America/Los_Angeles",
"currently": {
"apparentTemperature": 87.99,
"nearestStormDistance": 8,
"windGust": 10.26,
"windSpeed": 6.29,
"uvIndex": 11,
"visibility": 10,
"cloudCover": 0.15,
"icon": "clear-day",
"ozone": 303.81,
"precipIntensity": 0,
"summary": "Clear",
"time": 1532635571,
"humidity": 0.56,
"temperature": 84.9,
"windBearing": 221,
"dewPoint": 67.59,
"nearestStormBearing": 98,
"precipProbability": 0,
"pressure": 1013.35
},
"latitude": 33.8148455
},
"seq": "2018726000000005612",
"time": "2018-07-26T20:06:11.456058885Z",
"uuid": "7bbb1b5b-a360-44bb-bd2e-9c0cce898623"
},
"clientIp": "192.168.247.255",
"beat": {
"name": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"hostname": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"version": "7.0.0-alpha1"
}
}
},
{
"_index": "wx-rtbeat-2018.07",
"_type": "doc",
"_id": "p_802GQB4YMKAkYmxLi4",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"@timestamp": "2018-07-26T20:08:13.263Z",
"clientIp": "192.168.247.255",
"beat": {
"name": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"hostname": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"version": "7.0.0-alpha1"
},
"type": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"rxtxMsg": {
"seq": "2018726000000005613",
"time": "2018-07-26T20:08:11.893558485Z",
"uuid": "4fe80f2b-54d2-4df6-8b60-e9152e4c2754",
"producer": "cron",
"label": "/wx-data",
"key": "collector",
"payload": {
"currently": {
"pressure": 1013.33,
"uvIndex": 11,
"windSpeed": 6.35,
"precipIntensity": 0,
"time": 1532635691,
"visibility": 10,
"windBearing": 221,
"humidity": 0.56,
"nearestStormBearing": 98,
"nearestStormDistance": 8,
"ozone": 303.8,
"windGust": 10.3,
"cloudCover": 0.15,
"precipProbability": 0,
"summary": "Clear",
"apparentTemperature": 88.08,
"dewPoint": 67.58,
"icon": "clear-day",
"temperature": 84.99
},
"latitude": 33.8148455,
"longitude": -117.826581,
"offset": -7,
"timezone": "America/Los_Angeles"
}
}
}
},
{
"_index": "wx-rtbeat-2018.07",
"_type": "doc",
"_id": "qP822GQB4YMKAkYmc7hg",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"@timestamp": "2018-07-26T20:10:03.510Z",
"beat": {
"name": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"hostname": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"version": "7.0.0-alpha1"
},
"type": "wx-rtbeat-f744b8497-ch4ln",
"rxtxMsg": {
"label": "/wx-data",
"key": "collector",
"payload": {
"currently": {
"nearestStormDistance": 8,
"pressure": 1013.31,
"summary": "Clear",
"windBearing": 221,
"windGust": 10.33,
"humidity": 0.56,
"precipIntensity": 0,
"time": 1532635802,
"visibility": 10,
"icon": "clear-day",
"dewPoint": 67.57,
"nearestStormBearing": 98,
"uvIndex": 11,
"windSpeed": 6.4,
"cloudCover": 0.15,
"ozone": 303.79,
"precipProbability": 0,
"temperature": 85.06,
"apparentTemperature": 88.16
},
"latitude": 33.8148455,
"longitude": -117.826581,
"offset": -7,
"timezone": "America/Los_Angeles"
},
"seq": "2018726000000005614",
"time": "2018-07-26T20:10:02.217602453Z",
"uuid": "9e10b07e-d618-4c71-940a-8634d35db682",
"producer": "cron"
},
"clientIp": "192.168.247.255"
}
}
]
}
}
Explore the Elasticsearch official documentation: Search in Depth.
Port Forwarding / Local Development
Check out kubefwd for a simple command line utility that bulk forwards services of one or more namespaces to your local workstation.
Resources
- Setup a Custom Kubernetes Production Hobby Cluster for a more production-like development environment.
- Implement Kubernetes Team Access - RBAC for developers and QA to use
kubectlfor token-based authentication for developing locally with remote clusters. - Setup Production Grade Elasticsearch on Kubernetes for development, testing and production.
- Install Kibana on Kubernetes for Elasticsearch data browsing and visualization.
- Support High Traffic JSON Data into Elasticsearch on Kubernetes with rxtx and rtBeat.
This blog post, titled: "Remote Query Elasticsearch on Kubernetes: Local workstation-based microservices development" by Craig Johnston, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
